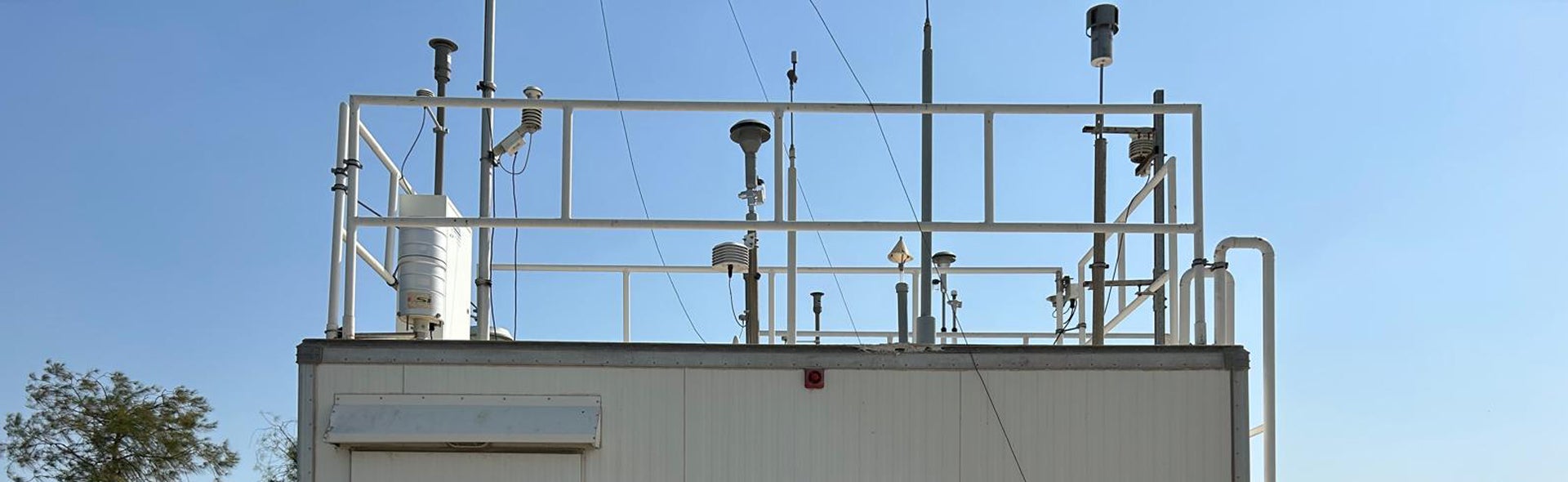
Overview
Research on atmospheric processes affecting air quality, solar radiation, and climate change in Qatar, generating region-specific evidence on environmental and human health impacts to inform policies and enhance national resilience.
Projects

The ambient air quality project is a strategic research effort designed to help improve air quality and mitigate the adverse impacts of air pollution on public health and the national economy in Qatar. It provides knowledge, national capability, and research-based evidence to inform the development of intervention policies for this purpose. It is composed of multiple connected research work packages linking sources of pollutants with atmospheric chemistry and meteorological processes. Ongoing research within this project contributes to benchmarking, revising, and developing national standards and guidelines for ambient air quality in Qatar. In collaboration with partners and stakeholders, the project is providing technical expertise in the assessment of the environmental factors determining the human health and economic impacts of air pollution in Qatar and urbanised arid regions. The project team has established very strong links with a wide range of national stakeholders, including the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change, the Ministry of Public Health, and Qatar Meteorology Department. The project includes basic and applied research components and heavily relies on the Air Quality Research Network, together with the enhanced aerosol research capabilities at key selected stations, for the delivery of both components of this project.
The Indoor Air Quality and Exposure Assessment project is a three-year study that establishes the first integrated baseline of indoor air quality (IAQ) and personal exposure in Qatar’s built environment. Using calibrated low-cost sensors, the project benchmarks IAQ across the Education city buildings, evaluates the influence of HVAC systems, occupancy, and outdoor infiltration, and quantifies personal exposure across multiple microenvironments. The work delivers validated sensor calibration models (WP1), baseline IAQ profiles and best-practice management strategies (WP2), and spatio-temporal exposure models with policy-relevant insights (WP3). The outcomes will support evidence-based IAQ standards, inform public health protection, and enable cross-disciplinary collaboration on sustainable building design and environmental technologies, directly contributing to Qatar’s national health and sustainability goals.

This research project aims to assess, model, and mitigate the impacts of climate change in Qatar and the Arabian Peninsula through an integrated approach, combining observational analysis, regional climate modeling, future projections, and adaptive heat mitigation strategies in the coastal, desert, and urban environment of Doha. This project begins by analyzing long-term variability in climate hazards such as temperature trends, precipitation shifts, sea level rise, and extreme weather events using data from meteorological stations, satellites, and global datasets to ensure data accuracy for subsequent modeling efforts. A high-resolution regional climate model (CLWRF) will be deployed to simulate past climate conditions, assess urban ambient conditions, and capture the impact of Doha’s urban morphology on the local climate. These simulations will serve as a basis for developing future climate projections spanning 2030 to 2100, evaluating shifts in temperature, precipitation patterns, and extreme events under various greenhouse gas emission scenarios. Building on these projections, the research will focus on assessing the effects of climate change on Doha’s outdoor thermal environment, air and surface temperatures, and building cooling demand. Furthermore, it will model and simulate heat mitigation strategies tailored to the urban morphology of Doha, such as green infrastructure, cool materials, and shading, to enhance outdoor thermal comfort and reduce cooling energy consumption. The findings will support the formulation of evidence-based recommendations for policymakers and urban planners to improve urban resilience and align with Qatar’s sustainability goals under the 2030 national vision.
This project is designed to advance solar radiation research and applications in Qatar, with a focus on providing and characterizing solar resources and relevant atmospheric parameters for solar radiation forecasting, urban planning, climate, atmospheric, and agricultural applications. These efforts are essential contributions to sustainable solutions that enhance resilience and well-being in Qatar.
The research will focus on a detailed characterization of solar radiation and its variability across Qatar, including the analysis of key atmospheric parameters such as spectral irradiance, albedo, UV, long-wave IR, PAR radiation, and aerosols. The project will also support the development of applications for rooftop PV and solar forecasting techniques.
Additionally, it will explore solar radiation applications beyond electricity generation, with a focus on agriculture and environmental studies. The datasets generated, consisting of high-resolution solar data that incorporate the effects of dust and atmospheric variability, will be integrated into agricultural adaptation models to refine estimates of PAR, crop growth, evapotranspiration, and irrigation demand. In greenhouse farming, these datasets will inform studies of crop productivity, operational maintenance, and potential pathways for material optimization. In urban planning, they will support analyses of the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect by providing inputs to models of solar-driven heating in urban environments. Together, these applications demonstrate how solar resource assessment contributes to agriculture and environmental adaptation strategies. In summary, this project aims to deliver valuable insights into solar radiation resources and atmospheric influences, supporting research, informed decision-making, and applications across multiple fields within QEERI and various sectors in Qatar.

This project aims to advance the understanding and management of air pollution in Qatar and the region by developing a comprehensive modeling framework that integrates regional and local scales. The research is structured into four work packages (WPs):
WP1 focuses on the operational forecasting of dust and air quality, combining high-resolution meteorology and chemistry models to predict pollutant levels and dust storms. This forecasting system will deliver actionable insights to support public health and policymaking.
WP2 investigates the photochemical processes driving air quality, with sensitivity studies on emissions, meteorological factors, and secondary pollutant formation. By identifying key drivers, this work will guide strategies for reducing harmful pollutants like ozone and secondary aerosols.
WP3 develops high-resolution spatial maps of primary pollutants, using detailed emission inventories. These maps will identify pollution hotspots, enabling targeted interventions to improve air quality.
WP4 employs micro-scale dispersion modeling to assess pollutant behavior in urban environments. By simulating localized pollution dynamics in areas like traffic corridors and densely populated neighborhoods, this work will inform urban planning and mitigation strategies.
The project will produce tools and datasets for air quality forecasting, mapping, and exposure assessment, contributing to sustainable urban development and public health protection. This research aligns with Qatar’s environmental priorities and offers a scalable framework for other regions facing similar challenges.
